Data Preparation¶
The workflow does not directly incorporate data preparation options; such preparations must be performed beforehand. Effective data preparation might involve replacing missing values with specific estimates, performing interpolations, calculating distances to geological features, or creating geochemical indices. This process demands geological expertise and is essential for achieving reliable outcomes.
Additionally, this phase encompasses data augmentation, which entails generating new, relevant layers of data. The careful preparation and enhancement of data are fundamental steps that significantly contribute to the robustness and accuracy of the results obtained from the workflow.
No-Data Values¶
No-data values are a limitation in nearly all data science workflows. A point that contains at least one no-data value cannot be used by most machine learning algorithms. To address this, users must define a strategy for handling missing data—such as replacing no-data values with the mean, applying interpolation, or discarding affected points entirely. This applies to any property, including those used as model inputs or as the target variable.
In particular, the property used as the target must not contain too many no-data values. If a point has a missing value in the target, it will be excluded from the prediction process. To ensure that most of the points are eligible for prediction, missing values should be replaced with a defined value beforehand. This preprocessing step must be performed upstream in Geoscience ANALYST using the “Replace No-Data Values” function.
To replace missing values in Geoscience ANALYST, select the target data, right-click, and choose Replace No Data Value (A in Figure 2). In the panel that opens, specify the replacement value (e.g., 0; B in Figure 2).
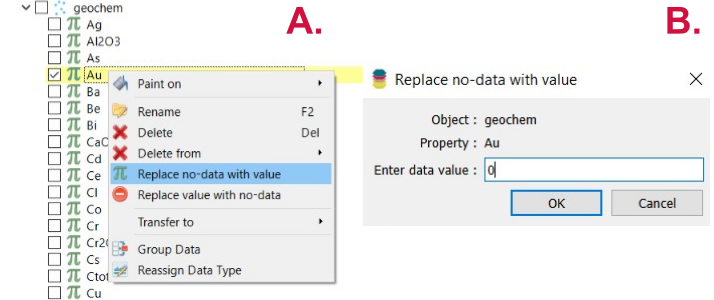
Figure 2 Change the No-Data values of the target.¶
Similarly, if a point contains a no-data value for any of the selected properties, it will be excluded from the modeling process. However, properties can be manually deselected in the workflow, and those with too many no-data values are automatically deselected by default. Still, it remains essential to review and manage missing values before running the analysis.
Data Augmentation¶
Data augmentation to obtain new data layers can be conducted in Geoscience ANALYST. The distance to specific objects, like faults, can be computed using the Calculate Distance Between Object option, available by right-clicking on the selected object. Geophysical data can be transferred using the Utilities/Transfer Data tool. Lastly, new layers, like mineral alteration indices, can be calculated using the Script utility available when right-clicking on the desired object.
